L1/L2
What networks are Layer 1 (L1) or Layer 2 (L2)
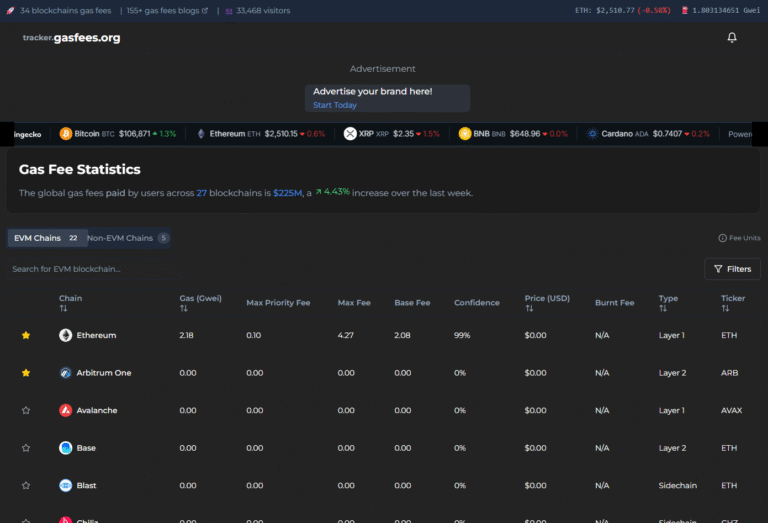
In the blockchain ecosystem, understanding gas fees—the transaction costs paid for operations on a blockchain—is essential. They not only affect the user experience but also reflect the scalability and efficiency of different blockchains.
Here’s an overview of the gas fees associated with Layer 1 (L1) and Layer 2 (L2) blockchains.
Layer 1 Blockchains: The Foundation
Layer 1 blockchains operate as standalone networks with their own native tokens. Gas fees on these blockchains vary based on factors like transaction volume, network congestion, and block size.
Examples of L1 Blockchains and Their Gas Fees
- Ethereum Gas Fees: Known for high fees during peak usage; fees are paid in ETH.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC) Gas Fees: Lower fees compared to Ethereum, paid in BNB.
- Solana Gas Fees: Extremely low fees, leveraging high throughput.
- Avalanche Gas Fees: Competitive fees, paid in AVAX.
- Polygon Gas Fees: Affordable, though Polygon also provides L2 solutions.
- Fantom Gas Fees: Low fees, optimized for DeFi applications.
- Hedera Gas Fees: Predictably low, paid in HBAR.
- NEAR Gas Fees: Cost-effective, with a focus on user-friendly scalability.
- Harmony Gas Fees: Low fees, paid in ONE, with a sharding-based structure.
- Tezos Gas Fees: Minimal, with a governance-first approach.
Layer 2 Solutions: Enhancing Scalability
Layer 2 solutions are designed to alleviate congestion and reduce fees on L1 blockchains by processing transactions off-chain or using optimized mechanisms.
Examples of L2 Solutions and Their Gas Fees
- Arbitrum Gas Fees: Lower fees for Ethereum transactions, utilizing rollups.
- Optimism Gas Fees: Affordable, designed for DeFi and dApps.
- zkSync Gas Fees: Focused on zk-rollups for lower costs.
- Polygon zkEVM Gas Fees: A cutting-edge Ethereum L2, highly scalable.
- Aurora Gas Fees: Cost-efficient as an L2 solution for NEAR.
- Moonbeam Gas Fees: Operates as a Polkadot parachain with competitive fees.
- Milkomeda Gas Fees: A sidechain often treated as an L2, bridging ecosystems.
Why Gas Fees Matter
Gas fees directly impact user adoption and developer engagement. Lower fees often attract more users, while high fees can discourage smaller transactions or experimentation with dApps. Both L1 and L2 solutions are critical in achieving the balance between decentralization, security, and scalability—the blockchain trilemma.
Stay Updated on Gas Fees
As blockchain technology evolves, so do the dynamics of gas fees. Platforms like GasFees.org are here to keep you informed, helping you navigate these costs across multiple blockchains and solutions.
Explore More:
- Compare fees across chains to optimize your transactions.
- Understand the role of rollups and sidechains in reducing costs.
Let us guide you through the ever-changing world of blockchain gas fees!
For more updates and detailed insights, visit GasFees.org.